Kenya Coffee School (KCS)
Welcome to Kenya Coffee School
Kenya Coffee School : Sustainable Knowledge for Every Stage of Your Barista and Specialty Coffee Career
Kenya Coffee School Training Levels : Certificate / Diploma / Advanced Diploma / Micro-Masters / Coffee MBA
The KCS’s Diploma Coffee Skills Program consists of education in the following specialties within the coffee industry:
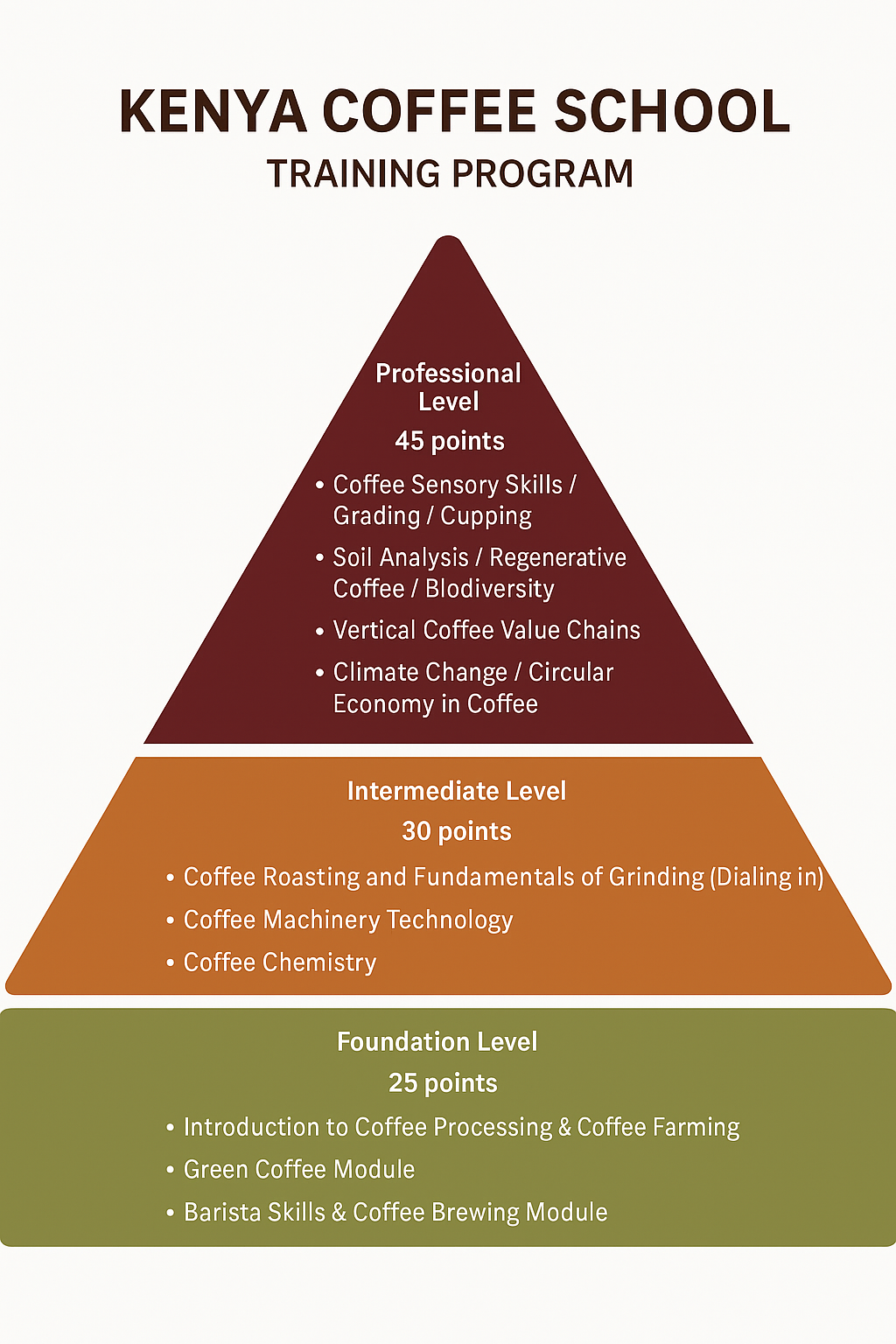
- Introduction to Specialty Coffee Processing & Coffee Farming
- Barista Skills – Latte art / International Recipes
- Coffee Brewing Module
- Green Coffee Module
- Sustainable Coffee Management
- Coffee Sensory Skills / Grading / Cupping
- Coffee Roasting Education
- Coffee Machinery Technology
- Coffee Chemistry
- Soil Analysis / Regenerative Coffee /Biodiversity
- Vertical Coffee Value Chains / Applied Sciences
- Climate Change / Circular Economy in Coffee
- Coffee Apprenticeship / Entrepreneurship / Customer service
- Mixology / Bartender Courses / Tea and Kombucha
- Gastronomic Sciences and Coffee Health Sciences
- GIS Technology and Mapping Traceability in Coffee
- Specialty Coffee Micro Biology, Botany and Physics
- Coffee Trade Certification Registration / Requirements and Compliance e.g. G4T, EUDR and Others
- Pastry, Gelato Ice creams, Chocolates and Coffee Confectionery
- KCS Coffee Branding and Sales & Marketing
- Coffee Innovation and Innovative Management Systems (IMS)
- POS / CRM / BI / ERPs for HORECA Systems
- Digital Inclusivity and Life Skills for Youth in Coffee
- HACCP Education Food Handlers Training
- First Aid Education & Coffee Safety in work places
- Sustainable Coffee Supply Chain Management Education
- Good Factory Management Practices, Governance in Coffee Cooperatives of the Quality Infrastructure in the context of a Quality Policy and a sustainability strategy
- Fundamentals of Sustainable Coffee Trade and Logistics in the age of Digital Information
- Coffee and Storytelling Education
- Coffee Logistics Module (Import / Export) / Direct Trade of Green and Roasted Coffee
- Film Making and Coffee Aromatic Linguistics & Expressions Module
- Coffee Livelihoods, SDGs and Community Development Education
- Coffee and Bees / Honey Production and Apitherapy
- Digital Coffee Skills for the Youth : Cyber Security, AI, IOT, and Blockchain Technologies
- Kenya Coffee School Business and Policy Law Studies
- The Art of Coffee International Negotiations
- Implementing a Coordinated Criminal Justice Response to Gender-based Violence Against Women Course (Women in Coffee Equality)
- Good Trade Certification (G4T) Studies – Beyond Fairness
- Coffee Livelihoods in Community Development
- Certificate (3 months) and Diploma (5 months) in Events Management, Hospitality Management and Gastronomy
Together these modules of learning are known as the KCS Skills Program. Students can take advantage of learning through three stages of knowledge and skills in each module: Foundation, Intermediate and Professional Coffee Skills.
Modules and Levels
The KCS Coffee Skills Program consists of six different modules: Introduction to Coffee, which is available at one level, and five specialist modules; Barista Skills, Brewing, Green Coffee, Roasting and Sensory Skills,
Each of the specialist modules is available at three different levels, with points attached at every stage. You may choose the modules that fit your interests and needs. Once you have achieved 100 points, you will be awarded the KCS Coffee Skills Diploma certified by Kenya Coffee School Lavazza Certified Trainer.
KCS has 12 Modules + 3 Mandatory Extra Courses as outlined above
KCS have 3 Main Category Levels of Studies :
KCS Foundation Level: 25 Points
KCS Intermediate Level: 30 Points
KCS Professional Level: 45 Points
Enroll Today :
COOPERATIVE BANK : MPESA PAYBILL : 400200
ACCOUNT : 842788
RECEIVED BY ACCOUNT NAME : KENYA COFFEE SCHOOL
*Specialty Coffee Diploma costs : Ksh.47,000/- + : *Certificate Level : 34,500/- *KCS *Mixology / Bartender : 32,500/-
(Duration of Study 4 to 8 Weeks)
Maps Generator
Important News Around Coffee and Coffee Events
Find Us Via Map : Directions
Follow Kenya Coffee School on Instagram

KENYA COFFEE SCHOOL™
Digital Badges & Certificates Verification System



☕ Kenya Coffee School – the leading institution for Barista Skills, Specialty Coffee, and Mixology Training in Kenya. We offer internationally recognized programs designed to equip you with world-class coffee and beverage expertise.
🎓 Courses & Fees
Barista and Specialty Coffee
Barista & Specialty Coffee Certificate Level (Barista Mtaani) — KES 25,000
Specialty Coffee Foundation Diploma Level — KES 35,000 (5–6 weeks)
Specialty Coffee Intermediate Diploma Level — KES 64,000 (8–9 weeks)
Specialty Coffee Professional Diploma Level — KES 89,000 (11–12 weeks)
Mixology / Bartender : KES 30,000/-
🍹 Combined Offer
Barista Skills + Specialty Coffee + Mixology — KES 65,000
💰 All fees payable in installments and inclusive of exams and certification.
🌱 Advanced Coffee #Courses / Micro Masters Level
Coffee Value Analysis (CVA) — KES 78,000 (2 weeks)
KCS-ABC™ Coffee Grading (Equivalent to Q Grading) — KES 84,000 (3 weeks)
KCS Coffee Micro-Masters Level 12 Months – KES 336,800/-
- Improving Coffee Quality Transparency and Farmer Income through the ABCVA™ System
 ABCVA™ Cooperative Economic Impact Report Improving Coffee Quality Transparency and Farmer Income through the ABCVA™ System Author: Alfred Gitau MwauraFounder – Kenya Coffee SchoolCreator – ABCVA™ Coffee Sensory Model Executive Summary The ABCVA™ Coffee Sensory Science System introduces a structured framework for evaluating coffee quality through five sensory pillars: Aroma, Balance, Complexity, Vibrancy, and Aftertaste. By implementing a standardized quality evaluation system, coffee cooperatives can strengthen transparency in coffee grading, improve communication with international buyers, and position their coffees more competitively within specialty markets. This report explains how theLearn More
ABCVA™ Cooperative Economic Impact Report Improving Coffee Quality Transparency and Farmer Income through the ABCVA™ System Author: Alfred Gitau MwauraFounder – Kenya Coffee SchoolCreator – ABCVA™ Coffee Sensory Model Executive Summary The ABCVA™ Coffee Sensory Science System introduces a structured framework for evaluating coffee quality through five sensory pillars: Aroma, Balance, Complexity, Vibrancy, and Aftertaste. By implementing a standardized quality evaluation system, coffee cooperatives can strengthen transparency in coffee grading, improve communication with international buyers, and position their coffees more competitively within specialty markets. This report explains how theLearn More - March 2026 Intake Social Media Campaign by Kenya Coffee School☕ March 2026 Intake Social Media Campaign Kenya Coffee School & Barista Mtaani Post 1 — Campaign Launch Visual: Coffee farm → roasting → barista → cupping collage Caption ☕ March 2026 Intakes Now Open Welcome to Kenya Coffee School & Barista Mtaani. Learn the complete coffee journey: 🌱 Coffee Farming⚙️ Coffee Processing🔥 Coffee Roasting☕ Coffee Brewing👃 Coffee Tasting Experience coffee from Cherry to Cup. 📍 Hills Moka Coffee Experience Center Join the March Intake. #KenyaCoffeeSchool #BaristaMtaani #CoffeeTrainingKenya Post 2 — The Kenyan Coffee Story Visual: Coffee farm inLearn More
- Understanding the Coffee ChemistryCabbage or Sulfury Off-Tastes in Coffee: Understanding the Chemistry By Kenya Coffee School Coffee is one of the most chemically complex beverages in the world. Scientists estimate that more than 1,500 volatile compounds contribute to the aroma and flavor of a cup of coffee. When properly cultivated, processed, roasted, and brewed, these compounds create the delightful sensory profile associated with specialty coffee—notes of chocolate, fruit, florals, and caramel. However, when something goes wrong during processing, roasting, or brewing, certain compounds can produce undesirable flavors. One of the most notableLearn More
- Where Can I Train for Barista in Kenya? (2026 Ultimate FAQ Guide)
 Where Can I Train for Barista in Kenya? (2026 Ultimate FAQ Guide) If you’re asking “Where can I train for barista in Kenya?”, you’re already on the right path toward joining one of the fastest-growing hospitality and specialty coffee careers in East Africa. Kenya is globally known for producing world-class coffee — but today, it’s also becoming a regional hub for professional barista training, specialty coffee education, roasting science, and coffee entrepreneurship. Below is a complete FAQ guide to help you choose the right school. ☕ Why Study BaristaLearn More
Where Can I Train for Barista in Kenya? (2026 Ultimate FAQ Guide) If you’re asking “Where can I train for barista in Kenya?”, you’re already on the right path toward joining one of the fastest-growing hospitality and specialty coffee careers in East Africa. Kenya is globally known for producing world-class coffee — but today, it’s also becoming a regional hub for professional barista training, specialty coffee education, roasting science, and coffee entrepreneurship. Below is a complete FAQ guide to help you choose the right school. ☕ Why Study BaristaLearn More - Why NPK 23:23:0 Might Not Work for Your Coffee🌱 Why NPK 23:23:0 Might Not Work for Your Coffee As someone deeply involved in Kenya’s coffee ecosystem, you already know that coffee is not just a crop — it is a nutrient-sensitive perennial tree. Using the wrong fertilizer formula can silently reduce yields, cup quality, and long-term soil health. One of the most commonly misapplied fertilizers in coffee farms is NPK 23:23:0. Let’s break down why this formula may not be suitable for your coffee. 🔬 Understanding NPK 23:23:0 NPK 23:23:0 means: At first glance, it looks balanced.Learn More
- Telling the Kenyan Coffee Story as it is!
 Alfred Gitau Mwaura Telling the Kenyan Coffee Story as it is! Kenya’s coffee story has often been told in export statistics, auction prices, and global specialty rankings. But according to Alfred Gitau Mwaura, the true Kenyan coffee story is deeper — rooted in farmers’ hands, youth innovation, culture, technology, and national identity. As Founder & Executive Secretary General of Kenya Coffee School and Founder of Barista Mtaani, Alfred Gitau Mwaura has positioned himself not just as an educator or entrepreneur, but as a custodian of Kenya’s coffee narrative. BeyondLearn More
Alfred Gitau Mwaura Telling the Kenyan Coffee Story as it is! Kenya’s coffee story has often been told in export statistics, auction prices, and global specialty rankings. But according to Alfred Gitau Mwaura, the true Kenyan coffee story is deeper — rooted in farmers’ hands, youth innovation, culture, technology, and national identity. As Founder & Executive Secretary General of Kenya Coffee School and Founder of Barista Mtaani, Alfred Gitau Mwaura has positioned himself not just as an educator or entrepreneur, but as a custodian of Kenya’s coffee narrative. BeyondLearn More
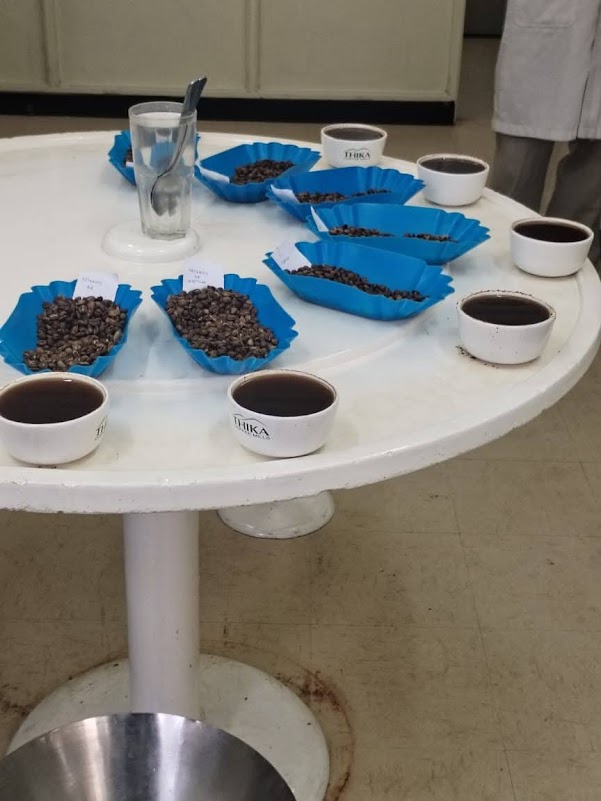








Share Your Achievement!
Celebrate your success by sharing your verified credentials.